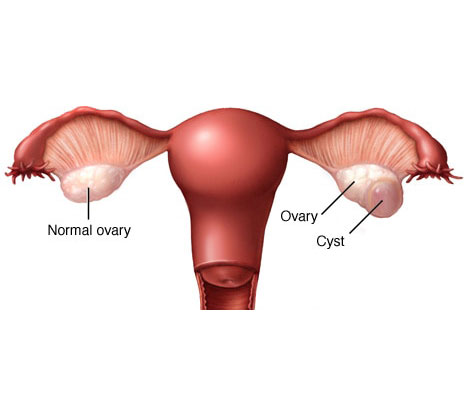
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. Often they cause no symptoms. Occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. If the cyst either breaks open or causes twisting of the ovary severe pain may occur. This may result in vomiting or feeling faint. The majority of cysts are, however, harmless.
Most ovarian cysts are related to ovulation being either follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. Other types include cysts due to endometriosis, dermoid cysts, and cystadenomas. Many small cysts occur in both ovaries in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Pelvic inflammatory disease may also result in cysts. Rarely cysts may be a form of ovarian cancer. Diagnosis is undertaken by pelvic examination with an ultrasound or other testing used to gather further details.
Some or all of the following symptoms may be present, though it is possible not to experience any symptoms:
Other symptoms may depend on the cause of the cysts:
