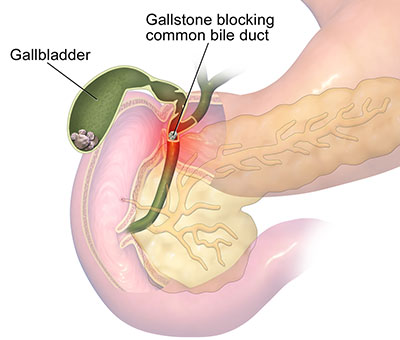
Gallbladder problems are usually caused by the presence of gallstones which are usually small and hard, consisting primarily of cholesterol and bile salts that form in the gallbladder or in the bile duct.
It is uncertain why some people form gallstones but risk factors include being female, prior pregnancy, age over 40 years and being overweight. Gallstones are also more common as you get older and some people may have a family history of gallstones.
There is no known means to prevent gallstones.
These stones may block the flow of bile out of the gallbladder, causing it to swell and resulting in sharp abdominal pain, vomiting, indigestion and, occasionally, fever.
If the gallstone blocks the common bile duct, jaundice (a yellowing of the skin) can occur.