Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. It may be acute or chronic. Appendicitis can occur at any time, but it occurs most often between the ages of 10 and 30. It’s more common in men than in women. Complications from appendicitis can be serious and even fatal.
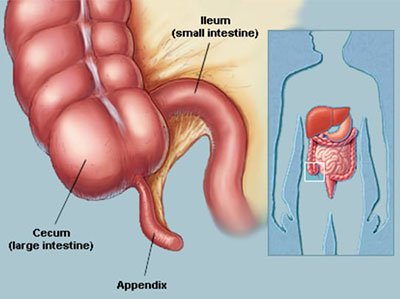
In many cases, the cause for appendicitis is unknown. There can also be multiple causes for any one case of appendicitis. Doctors believe that one cause of this condition an obstruction in the appendix. Obstruction may be either partial or complete. Complete obstruction is a cause for emergency surgery.
Obstruction is often due to an accumulation of fecal matter. It can also be the result of:
When there’s an obstruction in your appendix, bacteria can multiply inside the organ. This leads to the formation of pus. The increased pressure can be painful. It can also compress local blood vessels. A lack of blood flow to the appendix may cause gangrene.
If the appendix ruptures, fecal matter can fill the abdomen. This is a medical emergency.
Peritonitis is one possible consequence of a ruptured appendix. It’s an inflammation of the tissue that lines the abdominal wall. Other organs can also become inflamed after a rupture. Affected organs may include the cecum, bladder, and sigmoid colon.
If the infected appendix leaks instead of ruptures, it can form an abscess. This confines the infection to a small walled off area. However, an abscess can still be dangerous.
Symptoms of appendicitis include:
You may experience one or more of these symptoms. Appendicitis pain may start off as mild cramping. It often becomes more steady and severe with time. You won’t necessarily notice changes in your bowel habits. However, sometimes appendicitis can affect urination.
Treatment for appendicitis varies. In rare cases, appendicitis may get better without surgery. Treatment might involve only antibiotics and a liquid diet.
In most cases, however, surgery will be necessary. The surgical removal of the vermiform appendix is called an appendectomy. This removal is normally performed as an emergency procedure when the patient is suffering from acute appendicitis.
Now-a-days surgery is done laproscopically and patient can go home within 24-48 hours.
